Introduction
Air pollution is the most critical environmental problem of our era. With growing cities and industrialization, the air we inhale is becoming more and more poisonous. Knowing what are air pollutants, where they come from, and how they impact human health is important to tackle this emerging menace. Here in this blog, we are going to discuss the key air pollutants, how they affect the health of humans, and how to control air pollution efficiently, particularly keeping India in view.
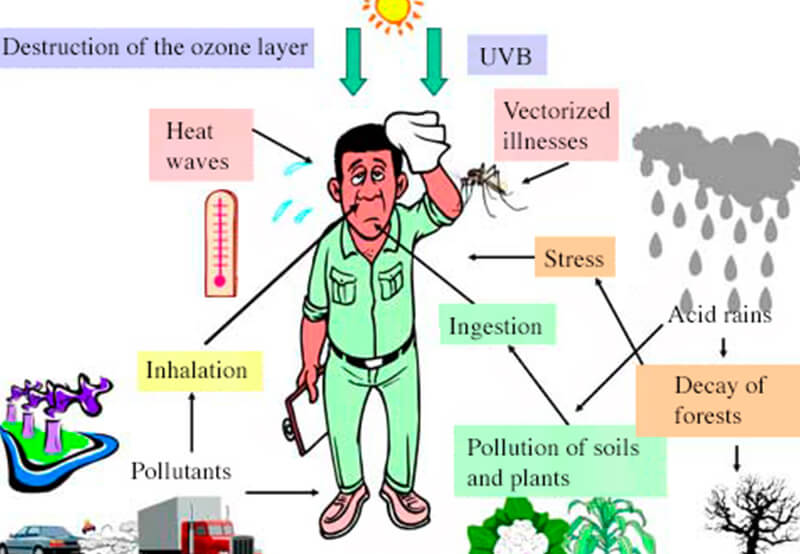
What Are Air Pollutants?
Air pollutants are chemicals present in the atmosphere that have the potential to cause damage to human health, the environment, or both. They can exist as gases, particulates, or bio molecules. They are classified into two main categories:
What Are Primary and Secondary Air Pollutants?
- Primary pollutants are emitted directly by sources like cars, industries, or natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions. Examples of such pollutants are carbon monoxide (CO), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), and nitrogen oxides (NOₓ).
- Secondary pollutants are not emitted directly but develop in the air by chemical reactions. Smog and ground-level ozone (O₃) are prime examples.
Key Air Pollutants
- Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10): These particles are fine enough that they can penetrate the lungs and bloodstream and cause respiratory and cardiovascular disease.
- Nitrogen Oxides (NOx): Generated mainly by automobiles and power generation, NOx forms smog and acid rain, and has the ability to irritate the lungs.
- Sulfur Dioxide (SO2): Emitted by oil and coal burning, SO2 can cause respiratory problems and trigger asthma.
- Carbon Monoxide (CO): Unfinished burning produces this colourless, odourless gas, which can reduce oxygen levels in vital organs.
- Ozone (O3): Ozone high in the atmosphere is harmless, but ground-level ozone forms from sunlight-driven reactions and has harmful, disease-causing effects.
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Typically used in paints, solvents, and fuel, VOCs are responsible for smog and result in long-term health issues.
Effects of Air Pollution on Human Health
The effects of air pollution on human health are widespread and severe:
- Respiratory Issues: Asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Cardiovascular Problems: Increased risk of heart attacks and strokes
- Cancer: Long-term exposure to air pollution is linked to lung and bladder cancer
- Neurological Effects: Emerging studies link air pollution to cognitive decline and developmental delays in children
- Premature Death: According to WHO, millions of premature deaths are linked to air pollution annually
Major Causes of Air Pollution in India
The effects of air pollution on human health are widespread and severe:
- Respiratory Problems: Asthma, bronchitis, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
- Cardiovascular Illnesses: Risk of heart attacks and strokes is increased
- Cancer: Air pollution that occurs over long periods is associated with lung and bladder cancer
- Neurological Impacts: New studies connect air pollution with a decline in thinking as well as developmental delays in children
- Early Death: WHO estimates that millions of early deaths are caused by air pollution every year
How to Reduce Air Pollution: Practical Steps
Improving air quality requires action at both the individual and policy levels. Here’s how to reduce air pollution:
- Use Public Transport or Electric Cars
- Encourage Use of Renewable Energy
- Prohibit or Restrict Crop Burning
- Implement Industrial Emission Regulations
- Increase Plantation of More Trees and Greenery
- Utilize Energy-Saving Appliances
- Create Awareness Through Education and Campaigns
Conclusion
Understanding the key air pollutants and their far-reaching consequences is the first step toward a healthier future. The effects of air pollution on human health are too critical to ignore, especially given the major causes of air pollution in India. By identifying what are primary and secondary air pollutants and taking proactive steps, we can all contribute to cleaner air and a safer environment. Let’s breathe better, live longer.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Air pollutants are harmful substances present in the atmosphere that can damage human health, ecosystems, and the climate. They include gases like carbon monoxide and nitrogen dioxide, as well as particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10).
Primary air pollutants are directly released from a source, such as vehicle exhaust or industrial emissions. Secondary air pollutants form in the atmosphere through chemical reactions, such as smog and ground-level ozone.
Key air pollutants include particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), sulfur dioxide (SO₂), nitrogen oxides (NOₓ), carbon monoxide (CO), ground-level ozone (O₃), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
The effects of air pollution on human health range from respiratory problems like asthma and bronchitis to heart disease, stroke, cancer, and even premature death. Children and the elderly are especially vulnerable.
Major causes of air pollution in India include vehicle emissions, industrial smoke, construction dust, crop residue burning, and the use of solid fuels in homes. Urban areas experience higher levels due to traffic and infrastructure growth.












